1. 创建项目
1.1 基本的项目结构了解
flutter create <project_name>创建后的 flutter 项目结构大概是:
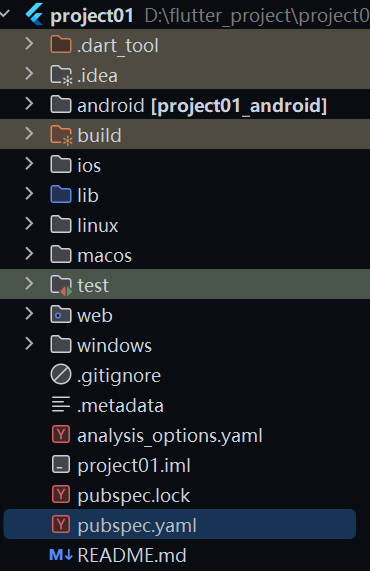
android 就是实现编译后的 android 代码,非我们的核心的编辑区域
ios 就是我们的编译后的 ios 的代码,也不是我们的核心的编码区域吧
linux 就是linux 应用的编译后的代码吧
windows web 同理吧
flutter 工程核心的代码和目录了解
pubspec.yaml就是我们的 flutter 的核心配置文件吧flutter pub getflutter pub upgradeflutter detector
pubspec.lock锁文件吧,锁定版本用的讷
我们的核心的代码区域就是我们的在 lib 目录下进行编写和完成吧,里面的就是我们的 dart 的文件吧
开发前需要注意的是将我们的镜像源换为 腾讯的或者说清华的镜像源进行开发,Google 的有一定的网络限制问题吧,这一点是需要进行注意的讷
1.2 核心代码浅读
pubspec.yaml就是进行配置的是我们的项目的讷
核心需要关注的是 dependencies 和 dev_dependencies 两个吧
一个是为了工程化需要做的工程化相关的东西吧
可能有:测试、打包构建优化的个性化配置、以及自动化的一些东西吧、以及代码质量限制的一些东西吧,以及其他的吧,核心就是工程化的一些东西以及个性化工程化的适配实现吧
在下面的案例中就给出了 flutter 工程的测试目录依赖 flutter_tests 和 flutter 代码质量检查的 flutter_lints
一个是核心的开发依赖
flutter flutter 开发核心的依赖文件吧
以及指定使用的 flutter 的特性配置吧
cupertino_icons icons 包吧
name: project01
description: "A new Flutter project."
# The following line prevents the package from being accidentally published to
# pub.dev using `flutter pub publish`. This is preferred for private packages.
publish_to: 'none' # Remove this line if you wish to publish to pub.dev
# The following defines the version and build number for your application.
# A version number is three numbers separated by dots, like 1.2.43
# followed by an optional build number separated by a +.
# Both the version and the builder number may be overridden in flutter
# build by specifying --build-name and --build-number, respectively.
# In Android, build-name is used as versionName while build-number used as versionCode.
# Read more about Android versioning at https://developer.android.com/studio/publish/versioning
# In iOS, build-name is used as CFBundleShortVersionString while build-number is used as CFBundleVersion.
# Read more about iOS versioning at
# https://developer.apple.com/library/archive/documentation/General/Reference/InfoPlistKeyReference/Articles/CoreFoundationKeys.html
# In Windows, build-name is used as the major, minor, and patch parts
# of the product and file versions while build-number is used as the build suffix.
version: 1.0.0+1
environment:
sdk: ^3.10.0
# Dependencies specify other packages that your package needs in order to work.
# To automatically upgrade your package dependencies to the latest versions
# consider running `flutter pub upgrade --major-versions`. Alternatively,
# dependencies can be manually updated by changing the version numbers below to
# the latest version available on pub.dev. To see which dependencies have newer
# versions available, run `flutter pub outdated`.
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
# The following adds the Cupertino Icons font to your application.
# Use with the CupertinoIcons class for iOS style icons.
cupertino_icons: ^1.0.8
dev_dependencies:
flutter_test:
sdk: flutter
# The "flutter_lints" package below contains a set of recommended lints to
# encourage good coding practices. The lint set provided by the package is
# activated in the `analysis_options.yaml` file located at the root of your
# package. See that file for information about deactivating specific lint
# rules and activating additional ones.
flutter_lints: ^6.0.0
# For information on the generic Dart part of this file, see the
# following page: https://dart.dev/tools/pub/pubspec
# The following section is specific to Flutter packages.
flutter:
# The following line ensures that the Material Icons font is
# included with your application, so that you can use the icons in
# the material Icons class.
uses-material-design: true
# To add assets to your application, add an assets section, like this:
# assets:
# - images/a_dot_burr.jpeg
# - images/a_dot_ham.jpeg
# An image asset can refer to one or more resolution-specific "variants", see
# https://flutter.dev/to/resolution-aware-images
# For details regarding adding assets from package dependencies, see
# https://flutter.dev/to/asset-from-package
# To add custom fonts to your application, add a fonts section here,
# in this "flutter" section. Each entry in this list should have a
# "family" key with the font family name, and a "fonts" key with a
# list giving the asset and other descriptors for the font. For
# example:
# fonts:
# - family: Schyler
# fonts:
# - asset: fonts/Schyler-Regular.ttf
# - asset: fonts/Schyler-Italic.ttf
# style: italic
# - family: Trajan Pro
# fonts:
# - asset: fonts/TrajanPro.ttf
# - asset: fonts/TrajanPro_Bold.ttf
# weight: 700
#
# For details regarding fonts from package dependencies,
# see https://flutter.dev/to/font-from-package
android 配置修改
核心需要关注的就是我们的分发的url进行设置一下吧,要不然依赖下载不下来讷
# 我的 flutter 的基本信息吧
Flutter 3.38.1 • channel stable • https://github.com/flutter/flutter.git
Framework • revision b45fa18946 (3 weeks ago) • 2025-11-12 22:09:06 -0600
Engine • hash 78c3c9557e50ee7c676fa37562558c59efd8406a (revision b5990e5ccc) (22 days ago) • 2025-11-12 21:08:24.000Z
Tools • Dart 3.10.0 • DevTools 2.51.1distributionBase=GRADLE_USER_HOME
distributionPath=wrapper/dists
zipStoreBase=GRADLE_USER_HOME
zipStorePath=wrapper/dists
distributionUrl=https://mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/gradle/gradle-8.13-bin.zip
2. Dart 语法总结
提前了解一下 dart 的基本语法,利于后续的看懂源码和含义吧,以及进行后续的一些架构拓展吧,这里也是简单总结一下吧,因为前面有一个文章已经讲过了的,哈哈
2.1 面向对象
class Person {
// 实现定义我们的属性吧
late String name;
late int age;
// 开始定义我们的构造函数吧
Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 以及是可以使用简化的构造分发的
// Person(this.name, this.age);
// 我们也可以定义一个命名构造函数
// Person.fromMap(Map<String, dynamic> map) {
// name = map['name'];
// age = map['age'];
// }
void sayHello() {
print('你好,我是$name,我今年$age岁');
}
}
class Vector {
final double x, y;
Vector(this.x, this.y);
// 操作符重载
Vector operator +(Vector v) => Vector(x + v.x, y + v.y);
Vector operator -(Vector v) => Vector(x - v.x, y - v.y);
// [] 操作符重载
double operator [](int index) {
if (index == 0) return x;
if (index == 1) return y;
throw RangeError.index(index, this, 'index', 'Vector只有2个分量', 2);
}
// == 操作符重载
@override
bool operator ==(Object other) =>
other is Vector && x == other.x && y == other.y;
@override
int get hashCode => Object.hash(x, y);
}2.2 定义变量
var 关键字定义变量
编译时的类型推断吧,实现的是根据初始化表达式在编译时确定类型吧
类型一旦通过推到确定后就是修改不了的讷:Dart 是强类型的语言吧,类型经过推断后就实现了固定
必须立即初始化实现吧,否则就会报错讷
核心是利用的 dart 的类型推导的原则吧,局部变量推荐的声明方式吧
var name = '张三';
var height;
// 这里就会报错了
// 因为 var 是需要进行立即初始化的
height = 1.8;
// var height = 18;final 关键字声明常量
运行时的一次性赋值,值在运行时进行赋值,但是只能进行赋值一次吧
内存和性能相比于 const 有更加灵活的内存使用模型吧
对象的可变性:final 值保证引用的不变,不实现保证对象内部的属性的不变性吧
类字段初始化时机:可以在声明时,构造函数的初始化列表或者构造函数体中进行对应的初始化操作吧
final 关键字声明的变量在内存中占有固定的位置,但是值是在运行时进行确定的讷
对于对象引用的话,引用地址不变,内部的属性变化是没有任何的问题的讷(除非对象本身是不可变化的讷)
final name = 'Dart'; // 类型推断为 String
final int count = 42; // 显式指定类型
// final 与对象可变性
final list = [1, 2, 3];
list.add(4); // 允许:list 引用不变,但对象内容可变
// list = [4, 5, 6]; // 错误:不能重新赋值
// final 类字段的不同初始化方式
class Example {
final String name;
final int count;
final List<int> numbers;
// 1. 构造函数初始化列表
Example(this.name) : count = 0, numbers = [];
// 2. 命名构造函数中的初始化
Example.another(String name) : this(name);
// 3. 初始化表达式
final DateTime createdAt = DateTime.now();
}
// final 的延迟初始化
class Database {
late final Connection _connection;
void initialize() {
_connection = Connection(); // 只能赋值一次
}
}const 编译时常量总结
编译时确定性:值必须在编译时可知吧
深度不可变性:const 创建的对象以及内部的内容都是不可变的讷
内存优化实现:相同值的 const 在对象上的内存模型是进行共享的讷
const 的值在编译是就被计算以及嵌入到代码中的讷
两个相同的 const 对象是同一个对象讷(canonicalized)
// const 的基本用法
const pi = 3.14159;
const int maxItems = 100;
// const 对象的不可变性
const list = [1, 2, 3];
// list.add(4); // 错误:const 列表不可变
// const 构造函数
class Point {
final double x, y;
const Point(this.x, this.y);
}
// 内存共享特性
const p1 = Point(1, 2);
const p2 = Point(1, 2);
print(identical(p1, p2)); // true:相同对象
// const 的递归不可变性
const complex = {
'list': const [1, 2, 3], // Dart 2+ 可以省略内部的 const
'point': const Point(0, 0),
};late 关键字使用
核心实现的是进行我们的延迟初始化值得操作吧
延迟时机的控制:允许非空变量延迟初始化吧
运行期进行检查实现:访问未初始化的 late 变量抛出错误吧
性能优化实现:避免不必要的初始化计算吧
和 final 结合后:创建只能初始化一次吧
懒加载模式实现吧
依赖注入模式的实现吧
循环依赖解决吧
// late 的基本用法
late String description;
void main() {
description = 'Dart is awesome!';
print(description);
}
// late 与 final 结合
class Temperature {
late final double _celsius;
late final double _fahrenheit;
void set celsius(double c) {
_celsius = c;
_fahrenheit = c * 9 / 5 + 32;
}
void set fahrenheit(double f) {
_fahrenheit = f;
_celsius = (f - 32) * 5 / 9;
}
}
// late 的懒加载模式
class HeavyObject {
late final ExpensiveObject _expensiveObject = ExpensiveObject();
ExpensiveObject get expensiveObject => _expensiveObject;
}
// late 的注意事项
class Example {
late int value;
void initialize() {
// 如果忘记调用 initialize(),访问 value 会抛出异常
value = 42;
}
void useValue() {
print(value); // 风险:可能访问未初始化的变量
}
}
// dynamic 的基本用法
dynamic variable = 'String';
variable = 42; // 允许:dynamic 可以重新赋值为不同类型
variable = Point(1, 2);
// dynamic 与 Object 的区别
Object obj = 'String';
// obj.length; // 错误:Object 没有 length 属性
dynamic dyn = 'String';
print(dyn.length); // 允许:运行时检查
// dynamic 的方法调用
dynamic value = 'hello';
print(value.toUpperCase()); // 运行时解析
// 类型检查操作符
dynamic something = 'test';
if (something is String) {
print(something.length); // 这里 something 被提升为 String
}
// JSON 处理中的 dynamic
Map<String, dynamic> json = {
'name': 'Dart',
'version': 2.12,
'features': ['null-safety', 'FFI']
};
// 风险:运行时错误
dynamic risky;
// print(risky.someMethod()); // 运行时抛出 NoSuchMethodError
// Object 作为通用类型
Object obj1 = 'String';
Object obj2 = 42;
Object obj3 = Point(1, 2);
// Object 的方法
print(obj1.hashCode);
print(obj2.runtimeType);
print(obj3.toString());
// 类型转换需要显式进行
Object stringObj = 'hello';
if (stringObj is String) {
String str = stringObj; // 自动类型提升
print(str.length);
}
// 泛型中使用 Object
List<Object> list = ['a', 1, true];
for (Object item in list) {
print(item.runtimeType);
}
// Object? 在空安全下的含义
Object? nullableObject = null; // 允许
nullableObject = 'now a string';2.3 数据结构
List(列表)
Set(集合)
Map(映射)
Queue(队列)
其他数据结构(如:LinkedList、DoubleLinkedQueue等,但较少使用)
2.3.1 List 数据结构
也就是我们的列表的数据结构吧
List<int> numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
var names = ["Alice", "Bob"] // 类型断言的声明形式吧
// 创建list的一些方法吧
List<int> fixedList = List.filled(5, 0);
List<int> generated = List.generate(5, (i) => i * 2);
List<int> unmodifiable = List.unmodifiable([1, 2, 3]);
// 空安全相关的
List<int?> nullable = [1, 2, null, 4];
List<int> nonNullable = [1, 2, 3];
// 常量列表
const List<int> constList = [1, 2, 3]; // 编译时运行吧
final List<int> finalList = [1, 2, 3]; // 运行时确定值吧核心的 api 总结吧
var list = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
// 基础访问
print(list[0]); // 10
print(list.first); // 10
print(list.last); // 50
print(list.length); // 5
print(list.isEmpty); // false
print(list.isNotEmpty); // true
// 安全访问
print(list.getRange(1, 4)); // (20, 30, 40)
print(list.sublist(1, 4)); // [20, 30, 40]
print(list.elementAt(2)); // 30
print(list.elementAtOrNull(10)); // null
print(list.firstWhere((n) => n > 25)); // 30
print(list.firstWhere((n) => n > 100, orElse: () => -1)); // -1
// 索引操作
print(list.indexWhere((n) => n > 25)); // 2
print(list.lastIndexWhere((n) => n > 25)); // 4
print(list.indexWhere((n) => n > 100)); // -1
var list = [1, 2, 3];
// 添加元素
list.add(4); // [1, 2, 3, 4]
list.addAll([5, 6]); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
list.insert(2, 99); // [1, 2, 99, 3, 4, 5, 6]
list.insertAll(2, [88, 77]); // [1, 2, 88, 77, 99, 3, 4, 5, 6]
// 移除元素
list.remove(99); // 移除第一个99,返回true
list.removeAt(0); // 移除索引0的元素,返回该元素
list.removeLast(); // 移除最后一个元素
list.removeRange(1, 3); // 移除索引1-2的元素
list.removeWhere((n) => n > 5); // 移除所有大于5的元素
// 替换元素
list[0] = 100; // 直接赋值
list.replaceRange(0, 2, [200, 300]); // 替换范围
list.fillRange(1, 3, 0); // 用0填充范围
var list = [1, 2, 3, 2, 4];
// 存在性检查
print(list.contains(2)); // true
print(list.contains(5)); // false
print(list.any((n) => n > 3)); // true
print(list.every((n) => n > 0)); // true
// 查找元素
print(list.where((n) => n > 2)); // (3, 2, 4) 注意:包含重复的2
print(list.where((n) => n > 2).toList()); // [3, 4]
print(list.singleWhere((n) => n == 3)); // 3
// print(list.singleWhere((n) => n == 2)); // 报错:有多个2
// 计数
print(list.length); // 5
print(list.where((n) => n > 2).length); // 3
var list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
// Map转换
var doubled = list.map((n) => n * 2); // (2, 4, 6, 8, 10)
var indexed = list.asMap(); // {0: 1, 1: 2, 2: 3, 3: 4, 4: 5}
// 转换为其他集合
Set<int> set = list.toSet(); // {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
List<String> strings = list.map((n) => n.toString()).toList();
// 展开操作
var nested = [[1, 2], [3, 4]];
var flattened = nested.expand((list) => list); // (1, 2, 3, 4)
// 折叠/归约
var sum = list.fold(0, (prev, n) => prev + n); // 15
var product = list.reduce((prev, n) => prev * n); // 120
var list = [5, 3, 1, 4, 2];
// 排序
list.sort(); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
list.sort((a, b) => b.compareTo(a)); // 降序 [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
// 创建新排序列表
var sorted = [...list]..sort(); // 不影响原列表
var reversed = list.reversed.toList(); // 反转
// 洗牌
list.shuffle(); // 随机打乱顺序
print(list); // 随机顺序
// 去重(通过转换为Set再转回)
var withDuplicates = [1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3];
var unique = withDuplicates.toSet().toList(); // [1, 2, 3]extension ListExtensions<T> on List<T> {
// 交换两个元素
void swap(int i, int j) {
var temp = this[i];
this[i] = this[j];
this[j] = temp;
}
// 分块
List<List<T>> chunk(int size) {
List<List<T>> chunks = [];
for (var i = 0; i < length; i += size) {
chunks.add(sublist(i, i + size > length ? length : i + size));
}
return chunks;
}
// 随机元素
T get random {
return this[Random().nextInt(length)];
}
}
// 使用
var list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
list.swap(0, 4);
print(list.chunk(2)); // [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5]]
print(list.random);组合代码
// 1. 选择合适的集合
// - 需要有序、允许重复:List
// - 需要唯一性、快速查找:Set
// - 需要键值对:Map
// - 需要双端操作:Queue
// 2. 预分配容量(性能敏感场景)
List<int> list = List.filled(1000, 0); // 预分配
Set<int> set = HashSet(capacity: 1000); // 预分配容量
// 3. 使用不可变集合
final immutableList = List.unmodifiable([1, 2, 3]);
final immutableSet = Set.unmodifiable({1, 2, 3});
final immutableMap = Map.unmodifiable({'a': 1, 'b': 2});
// 4. 利用扩展方法
extension CollectionExtensions<T> on Iterable<T> {
T? get firstOrNull => isEmpty ? null : first;
Iterable<T> distinct() {
final seen = <T>{};
return where((element) => seen.add(element));
}
Map<K, List<T>> groupBy<K>(K Function(T) keySelector) {
final map = <K, List<T>>{};
for (final element in this) {
final key = keySelector(element);
map.putIfAbsent(key, () => []).add(element);
}
return map;
}
}缓存实现
class Cache<K, V> {
final Map<K, V> _cache = {};
final Map<K, DateTime> _timestamps = {};
final Duration _ttl;
Cache({Duration? ttl}) : _ttl = ttl ?? const Duration(minutes: 5);
V? get(K key) {
if (!_cache.containsKey(key)) return null;
final timestamp = _timestamps[key]!;
if (DateTime.now().difference(timestamp) > _ttl) {
_cache.remove(key);
_timestamps.remove(key);
return null;
}
return _cache[key];
}
void set(K key, V value) {
_cache[key] = value;
_timestamps[key] = DateTime.now();
}
}分页
class Paginator<T> {
final List<T> _data;
final int _pageSize;
int _currentPage = 0;
Paginator(this._data, this._pageSize);
List<T> get currentPage =>
_data.sublist(
_currentPage * _pageSize,
(_currentPage + 1) * _pageSize > _data.length
? _data.length
: (_currentPage + 1) * _pageSize,
);
bool get hasNext => (_currentPage + 1) * _pageSize < _data.length;
bool get hasPrev => _currentPage > 0;
void next() => _currentPage++;
void prev() => _currentPage--;
}import type { PaginationOptions, PaginationInfo } from '../types/pagination';
/**
* data
* options
*/
export class EnhancedPaginator<T> {
// 首先定义需要维护的数据吧
private _data: T[];
private _pageSize: number;
private _currentPage: number;
private _selectedItems: Set<T> = new Set();
private _options: Required<PaginationOptions<T>>;
// 事件监听器吧
private _listeners: Set<(info: PaginationInfo<T>) => void> = new Set();
constructor(data: T[], options: PaginationOptions<T>) {
this._data = [...data]; // 实现浅拷贝一份吧
this._pageSize = options.pageSize || 10;
this._currentPage = (options.initialPage || 1) - 1; // 转换为 0-base的基准值的实现吧
this._options = {
pageSize: this._pageSize,
loop: options.loop || false,
maxPageButtons: options.maxPageButtons || 5,
onPageChange: options.onPageChange || (() => {}),
initialPage: options.initialPage || 1,
preserveSelection: options.preserveSelection || false
}
// 确保的是我们的当前的页码是合法有效的吧
/**
* @description 基本的原理是:
* @description 1. 确保当前的页码是在合法的范围内吧,合法范围就是: [0, totalPages - 1] 之间吧
* @description 2. 使用的确保API就是: Math 的 max 和 min 即可吧
*/
this._currentPage = Math.max(0, Math.min(this._currentPage, this.totalPages - 1));
}
/**
* @description 获取当前页的数据吧
* @returns 当前页的数据吧
*/
get totalPages(): number {
// 因为我们是 0-base 的实现,所以需要 +1 吧,这里就需要进行确保一下我们的 totalPages 是大于等于 1 吧
return Math.max(1, Math.ceil(this._data.length / this._pageSize));
}
/**
* @description 获取当前页的数据吧
* @description 核心的计算思路就是基于我们的当前的页码和每一页的大小来实现的吧
* @returns 当前页的数据吧
*/
get currentPageData(): T[] {
const startIndex = this._currentPage * this._pageSize;
/**
* @description 确保的是我们的 endIndex 不会超过我们的数组的长度吧
*/
const endIndex = Math.min(startIndex + this._pageSize, this._data.length);
return this._data.slice(startIndex, endIndex);
}
get info(): PaginationInfo<T> {
/**
* @description 核心的计算思路就是基于我们的当前的页码和每一页的大小来实现的吧
*/
const startIndex = this._currentPage * this._pageSize;
const endIndex = Math.min(startIndex + this._pageSize, this._data.length);
return {
currentPage: this._currentPage + 1,
totalPages: this.totalPages,
totalItems: this._data.length,
data: this.currentPageData,
itemsOnPage: this.currentPageData.length,
startIndex: this._data.length > 0 ? startIndex + 1 : 0,
endIndex: endIndex,
hasPrev: this.hasPrev,
hasNext: this.hasNext,
allData: [...this._data],
}
}
get hasNext(): boolean {
if (this._options.loop) {
return this._data.length > 0;
}
return (this._currentPage + 1) * this._pageSize < this._data.length;
}
get hasPrev(): boolean {
if (this._options.loop) {
return this._data.length > 0;
}
return this._currentPage > 0;
}
/**
* @description 获取当前选中的项吧
* @returns 当前选中的项吧
*/
get selectedItems(): T[] {
return Array.from(this._selectedItems);
}
// 开始实现处理我们的事件监听器的实现吧
subscribe(listener: (info: PaginationInfo<T>) => void) {
this._listeners.add(listener);
return () => this._listeners.delete(listener) as any;
}
private _notify() {
const info = this.info;
this._listeners.forEach(listener => listener(info));
this._options.onPageChange(info);
}
// 开始实现我们的核心的翻页逻辑吧
next(): void {
if (this.hasNext) {
if (this._currentPage < this.totalPages - 1) {
this._currentPage++;
} else if (this._options.loop) {
this._currentPage = 0;
}
this._notify();
}
}
prev(): void {
if (this.hasPrev) {
if (this._currentPage > 0) {
this._currentPage--;
} else if (this._options.loop) {
this._currentPage = this.totalPages - 1;
}
this._notify();
}
}
goToPage(page: number): void {
const targetPage = Math.max(1, Math.min(page, this.totalPages));
this._currentPage = targetPage - 1;
this._notify();
}
first(): void {
if (this.totalPages > 0) {
this._currentPage = 0;
this._notify();
}
}
last(): void {
if (this.totalPages > 0) {
this._currentPage = this.totalPages - 1;
this._notify();
}
}
private _isSameItem(a: T | any, b: T | any): boolean {
// 深度实现一下吧
if (a === b) {
return true;
}
if (a === null && b === null) {
return true;
}
if (a === null || b === null || typeof a !== "object" || typeof b !== "object") {
return false;
}
if (Array.isArray(a) && Array.isArray(b)) {
if (a.length !== b.length) {
return false;
}
return a.every(item => b.includes(item))
}
if (a.constructor !== Object || b.constructor !== Object) {
return false;
}
const aKeys = Object.keys(a) as Array<keyof T>;
const bKeys = Object.keys(b) as Array<keyof T>;
if (aKeys.length !== bKeys.length) {
return false;
}
for (const key of aKeys) {
if (!bKeys.includes(key) || !this._isSameItem(a[key], b[key])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
updateData(data: T[]): void {
// 实现更新数据吧
this._data = [...data];
if (this._options.preserveSelection) {
const newSelectedItems = new Set<T>();
this._selectedItems.forEach(item => {
const found = this._data.find(newItem => this._isSameItem(item, newItem));
if (found) {
newSelectedItems.add(found);
}
});
this._selectedItems = newSelectedItems;
} else {
this._selectedItems.clear();
}
if (this._currentPage >= this.totalPages && this.totalPages > 0) {
this._currentPage = this.totalPages - 1;
} else if (this.totalPages === 0) {
this._currentPage = 0;
}
this._notify();
}
filter(predicate: (item: T) => boolean): void {
const filteredData = this._data.filter(predicate);
this.updateData(filteredData);
}
sort(compareFn: (a: T, b: T) => number): void {
const sortedData = [...this._data].sort(compareFn);
this.updateData(sortedData);
}
selectAll(): void {
this._selectedItems = new Set(this._data);
this._notify();
}
clearSelection(): void {
this._selectedItems.clear();
this._notify();
}
toggleSelection(item: T): void {
if (this._selectedItems.has(item)) {
this._selectedItems.delete(item);
} else {
this._selectedItems.add(item);
}
this._notify();
}
isSelected(item: T): boolean {
return this._selectedItems.has(item);
}
getPageButtons(): (number | '...')[] {
const total = this.totalPages;
const current = this._currentPage + 1;
const maxButtons = this._options.maxPageButtons;
if (total <= maxButtons) {
return Array.from({ length: total }, (_, i) => i + 1);
}
let start = Math.max(1, current - Math.floor(maxButtons / 2));
let end = start + maxButtons - 1;
if (end > total) {
end = total;
start = Math.max(1, end - maxButtons + 1);
}
const buttons: (number | '...')[] = [];
for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) {
buttons.push(i);
}
if (start > 1) {
buttons.unshift('...');
buttons.unshift(1);
}
if (end < total) {
buttons.push('...');
buttons.push(total);
}
return buttons;
}
reset(): void {
this._currentPage = this._options.initialPage - 1;
this._selectedItems.clear();
this._notify();
}
setOptions(options: Partial<PaginationOptions<T>>): void {
this._options = { ...this._options, ...options };
if (options.pageSize !== undefined) {
this._pageSize = options.pageSize;
}
this._notify();
}
}
其他的数据结构
map
queue
record
等等吧