运行测试命令是
python main.py注意对于我们的macos linux 需要明确的指定我们的版本讷,这里进行区分一下吧
Python 数据类型
获取数据类型的方式
type()实现返回的数据格式为
<class 'str'><class 'int'>
isinstance()判断的是我们的什么是什么的实例来进行讨论的吧
基础数据类型
整数类型 int
浮点数类型: float
字符串类型: str
标准的数据类型有
Nunber 数字
String 字符串
bool 布尔类型
List 列表
Tuple 元组类型
Set 集合类型
Dictionary 字典类型
Bytes 不可变的二进制数据吧
六个基本的数据类型的分类
基础数据类型(不可变类型): Number String Tuple bool
可变数据类型(引用数据类型):List Set Dictionary
对比实现:就是我们的 python 的话和 javascript 是一样的内存管理模型吧
但是也是具备差异化的讷
就是我们的javascript的字符串的操作的话是值类型的,进行修改后的操作:拼接,+ 等操作,还是一个内存地址的引用
但是 python 的 string 是一个引用的,不可变得,此时修改后对应的内存地址也会发生变化讷
所以说 python 的数据类型的分类的话核心是进行的是可变和不可变的区分吧
#! /usr/bin/python3
# 实现书写我们的python 的命令行脚本吧
print(isinstance("", str)) # True
print(type("")) # <class 'str'>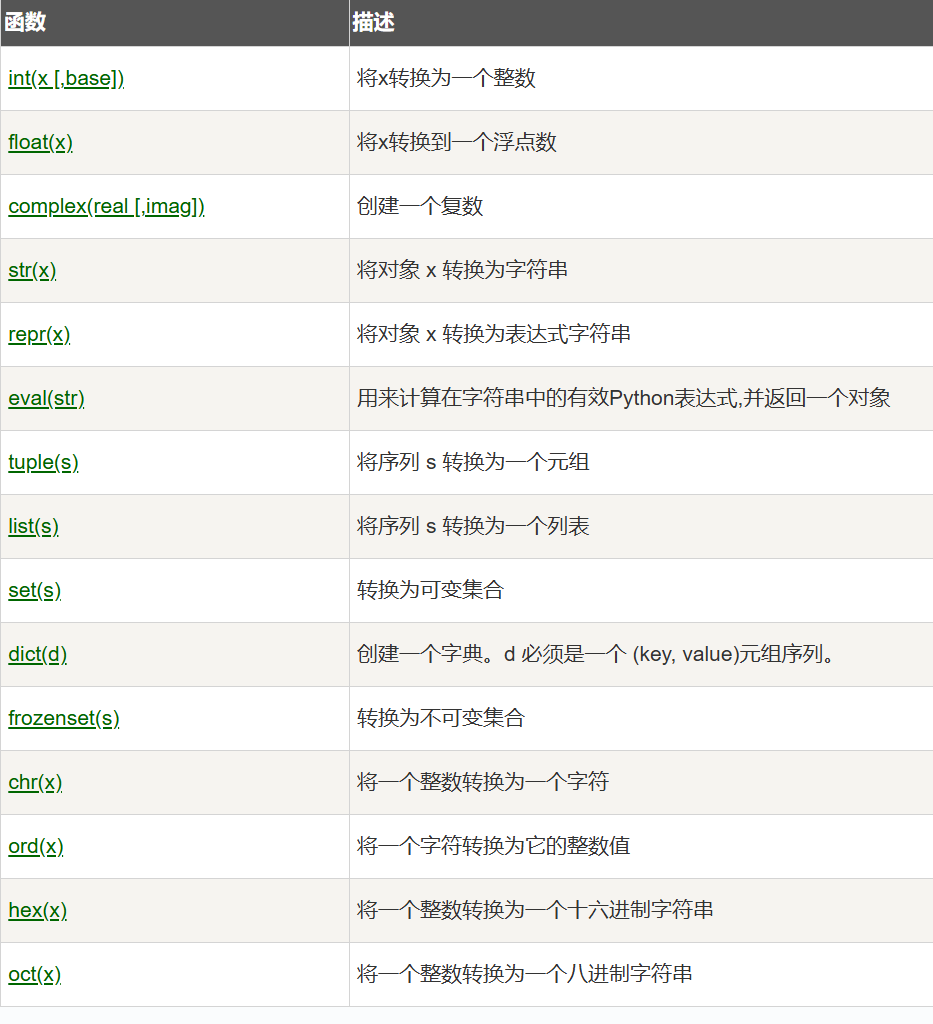
Python 运算符
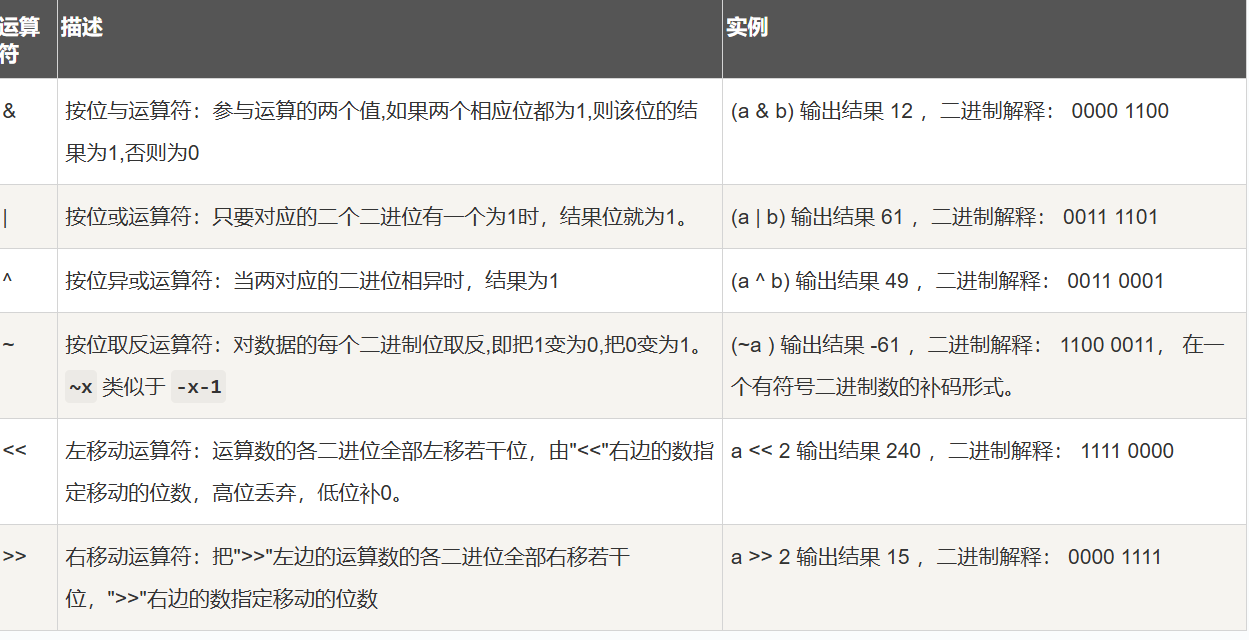
位运算符
逻辑运算符
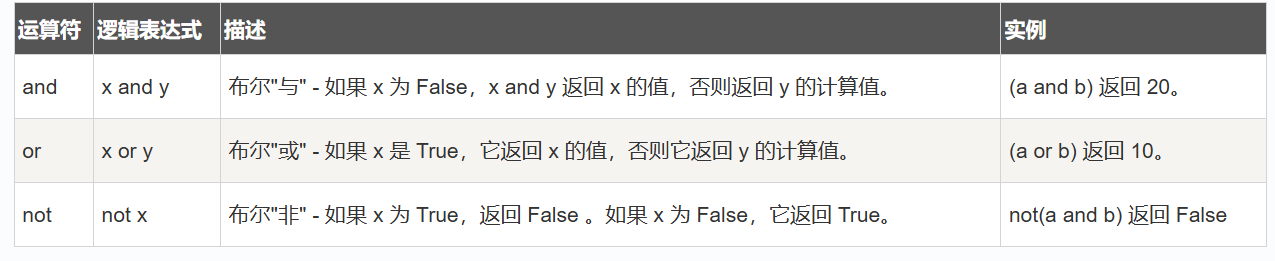
成员运算符
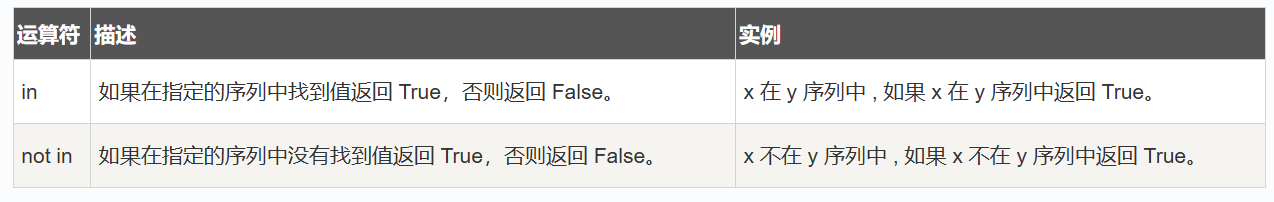
成员运算符
Python 数字
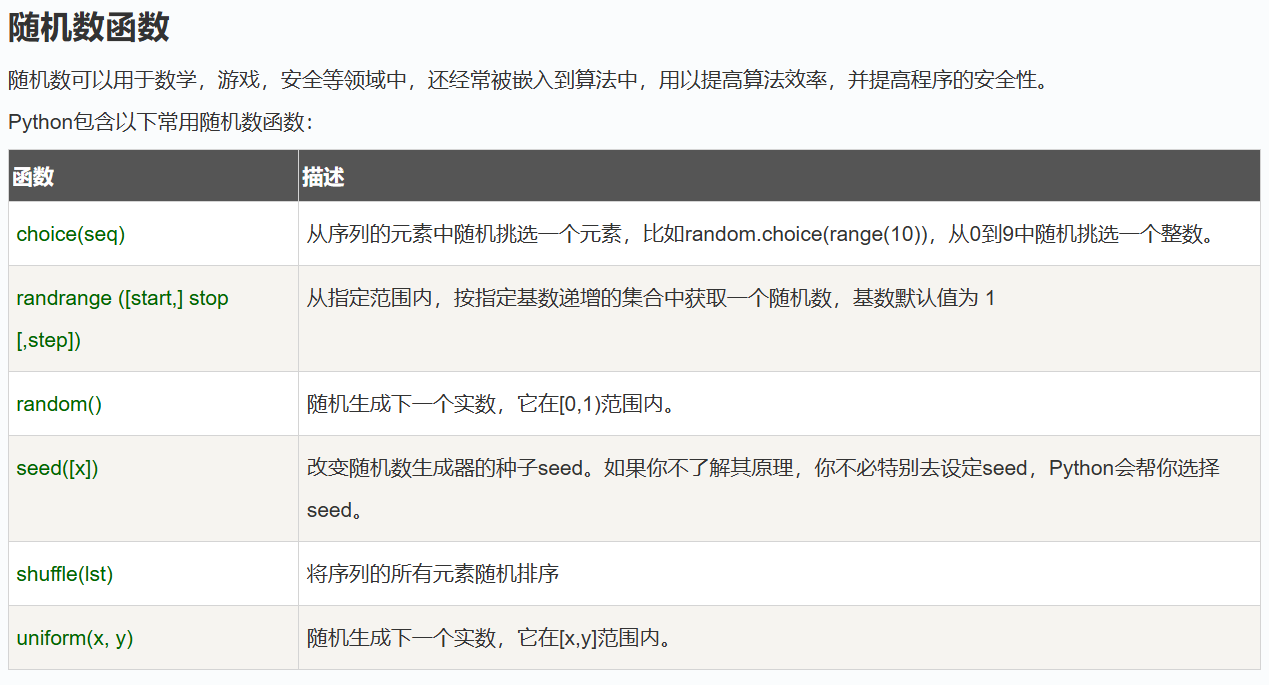
Python 字符串
Python List列表
Python 元组
元组是一个不可变的数据类型,所以说只是提供了对应的默认的属性操作吧
Python 字典
Python 推导式
实现的就是我们的过滤掉一些长度小于等于3的一些 element ,其他的直接进行转化为大写的操作吧
>>> names = ['Bob','Tom','alice','Jerry','Wendy','Smith']
>>> new_names = [name.upper()for name in names if len(name)>3]
>>> print(new_names)
['ALICE', 'JERRY', 'WENDY', 'SMITH']得到0-30 的整除3的数组吧
>>> multiples = [i for i in range(30) if i % 3 == 0]
>>> print(multiples)
[0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27]listdemo = ['Google','Runoob', 'Taobao']
# 将列表中各字符串值为键,各字符串的长度为值,组成键值对
>>> newdict = {key:len(key) for key in listdemo}
>>> newdict
{'Google': 6, 'Runoob': 6, 'Taobao': 6}Python 迭代器和生成器
核心的 api
iter()__iter__()next()__next__()
好处
节省内存:不需要一次性加载所有数据,而是按需生成或获取。
性能优化:可以在需要的时候才进行计算,避免不必要的计算。
可中断性:可以在任何点停止,比如我们可以在遍历到某个条件时提前终止,而不必处理整个数据集。
def infinite_sequence():
num = 0
while True:
yield num
num += 1
# 可以无限迭代,但通常不会真的无限迭代,会设置终止条件
for i in infinite_sequence():
if i > 100:
break
print(i)
def chunk_reader(file_path, chunk_size=1024):
"""分块读取文件"""
with open(file_path, 'rb') as file:
while True:
chunk = file.read(chunk_size)
if not chunk:
break
yield chunk
# 使用示例
for chunk in chunk_reader('large_binary_file.bin', 8192):
process_chunk(chunk)数据库查询优化
import psycopg2
from psycopg2 import pool
from contextlib import contextmanager
import json
class DatabaseStreamProcessor:
def __init__(self, db_config, pool_size=10):
self.db_pool = psycopg2.pool.SimpleConnectionPool(
1, pool_size, **db_config
)
@contextmanager
def get_cursor(self):
conn = self.db_pool.getconn()
try:
yield conn.cursor()
conn.commit()
except Exception:
conn.rollback()
raise
finally:
self.db_pool.putconn(conn)
def stream_large_query(self, query, params=None, chunk_size=1000):
"""流式处理大型查询结果,避免内存溢出"""
with self.get_cursor() as cursor:
cursor.execute(query, params or ())
while True:
rows = cursor.fetchmany(chunk_size)
if not rows:
break
# 对每一批数据进行处理
processed_chunk = self._process_rows(rows)
yield from processed_chunk
def _process_rows(self, rows):
"""处理单批数据,可以自定义业务逻辑"""
for row in rows:
# 模拟复杂的数据转换逻辑
processed = {
'id': row[0],
'data': json.loads(row[1]) if row[1] else {},
'timestamp': row[2].isoformat() if row[2] else None,
'processed_at': datetime.now().isoformat()
}
yield processed
def batch_update_generator(self, data_stream, batch_size=500):
"""将数据流分批用于批量更新"""
batch = []
for item in data_stream:
batch.append(item)
if len(batch) >= batch_size:
yield batch
batch = []
if batch: # 处理最后一批
yield batch
def process_user_analytics(self, start_date, end_date):
"""完整的用户分析数据处理管道"""
# 1. 流式读取用户行为数据
query = """
SELECT user_id, activity_data, created_at
FROM user_activities
WHERE created_at BETWEEN %s AND %s
ORDER BY created_at
"""
raw_stream = self.stream_large_query(query, (start_date, end_date))
# 2. 数据清洗和过滤
cleaned_stream = (
item for item in raw_stream
if item['data'].get('type') in ['purchase', 'view', 'click']
)
# 3. 数据聚合(按用户分组)
from collections import defaultdict
user_aggregates = defaultdict(lambda: {
'purchase_count': 0,
'view_count': 0,
'click_count': 0,
'total_value': 0.0
})
for item in cleaned_stream:
user_id = item['id']
activity_type = item['data'].get('type')
value = item['data'].get('value', 0)
if activity_type == 'purchase':
user_aggregates[user_id]['purchase_count'] += 1
user_aggregates[user_id]['total_value'] += float(value)
elif activity_type == 'view':
user_aggregates[user_id]['view_count'] += 1
elif activity_type == 'click':
user_aggregates[user_id]['click_count'] += 1
# 4. 生成最终分析结果
for user_id, aggregates in user_aggregates.items():
yield {
'user_id': user_id,
**aggregates,
'conversion_rate': (
aggregates['purchase_count'] / aggregates['view_count']
if aggregates['view_count'] > 0 else 0
)
}
# 使用示例
db_config = {
'host': 'localhost',
'database': 'analytics',
'user': 'user',
'password': 'password'
}
processor = DatabaseStreamProcessor(db_config)
# 处理大量用户数据
for user_stats in processor.process_user_analytics(
start_date='2024-01-01',
end_date='2024-01-31'
):
# 可以实时发送到消息队列或写入另一个数据库
print(f"User {user_stats['user_id']}: {user_stats}")服务器中间管道
import asyncio
from contextvars import ContextVar
from typing import Any, Callable, Awaitable, Generator
# 上下文变量,用于在中间件间传递数据
request_id_var = ContextVar('request_id', default=None)
class AsyncMiddlewarePipeline:
def __init__(self):
self.middlewares = []
def add_middleware(self, middleware_func: Callable):
self.middlewares.append(middleware_func)
async def process_request(self, request: dict) -> dict:
"""处理HTTP请求的中间件管道"""
# 创建处理管道
pipeline = self._build_pipeline(request)
# 执行管道
response = await pipeline.__anext__()
# 继续执行直到完成
async for _ in pipeline:
pass
return response
async def _build_pipeline(self, request: dict) -> Generator:
"""构建中间件处理管道"""
# 初始响应
response = {'status': 200, 'headers': {}, 'body': ''}
# 按顺序执行中间件
for middleware in self.middlewares:
# 每个中间件都是一个异步生成器
middleware_gen = middleware(request, response)
try:
# 执行中间件直到第一个 yield
await middleware_gen.__anext__()
# 中间件可以在这里修改request或response
yield response
# 继续执行中间件的剩余部分(响应处理)
try:
await middleware_gen.__anext__()
except StopAsyncIteration:
pass
except Exception as e:
print(f"Middleware error: {e}")
break
# 具体的中间件实现
async def auth_middleware(request: dict, response: dict):
"""认证中间件"""
# 请求处理阶段
token = request.get('headers', {}).get('authorization')
if not token or not await validate_token(token):
response['status'] = 401
response['body'] = 'Unauthorized'
return
user_id = await get_user_id_from_token(token)
request['user_id'] = user_id
# 让出控制权,继续执行下一个中间件
yield
# 响应处理阶段(可以在这里添加响应头等)
response['headers']['x-user-id'] = str(user_id)
async def logging_middleware(request: dict, response: dict):
"""日志记录中间件"""
import uuid
request_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
request_id_var.set(request_id)
# 记录请求开始
print(f"[{request_id}] Started {request['method']} {request['path']}")
start_time = asyncio.get_event_loop().time()
yield # 执行其他中间件和业务逻辑
# 记录请求完成
duration = asyncio.get_event_loop().time() - start_time
print(f"[{request_id}] Completed in {duration:.3f}s - {response['status']}")
async def rate_limit_middleware(request: dict, response: dict):
"""限流中间件"""
client_ip = request.get('client_ip')
if await is_rate_limited(client_ip):
response['status'] = 429
response['body'] = 'Too Many Requests'
return
yield
# 更新限流计数
await update_rate_limit(client_ip)
# 模拟的辅助函数
async def validate_token(token): return True
async def get_user_id_from_token(token): return 123
async def is_rate_limited(ip): return False
async def update_rate_limit(ip): pass
# 使用示例
async def main():
pipeline = AsyncMiddlewarePipeline()
pipeline.add_middleware(logging_middleware)
pipeline.add_middleware(auth_middleware)
pipeline.add_middleware(rate_limit_middleware)
# 模拟HTTP请求
request = {
'method': 'GET',
'path': '/api/data',
'headers': {'authorization': 'Bearer token123'},
'client_ip': '192.168.1.1'
}
response = await pipeline.process_request(request)
print(f"Final response: {response}")
# asyncio.run(main())监控收集
import time
import random
from collections import defaultdict, deque
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
class MetricsAggregator:
def __init__(self, window_size=300): # 5分钟窗口
self.window_size = window_size
self.metrics_buffer = deque(maxlen=window_size)
def metrics_generator(self, interval=1):
"""生成模拟的监控指标数据流"""
while True:
timestamp = datetime.now()
# 模拟多种监控指标
metrics = {
'timestamp': timestamp,
'cpu_percent': random.uniform(0, 100),
'memory_used': random.randint(1000, 8000),
'disk_io': random.randint(0, 1000),
'network_rx': random.randint(0, 1000000),
'network_tx': random.randint(0, 1000000),
'active_connections': random.randint(0, 10000)
}
yield metrics
time.sleep(interval)
def sliding_window_aggregator(self, metrics_stream, window_seconds=60):
"""滑动窗口聚合器"""
window = deque()
for metric in metrics_stream:
current_time = metric['timestamp']
# 移除过期的数据点
while (window and
(current_time - window[0]['timestamp']).total_seconds() > window_seconds):
window.popleft()
window.append(metric)
if len(window) > 0:
# 计算窗口内的聚合指标
aggregated = self._aggregate_window(list(window))
yield aggregated
def _aggregate_window(self, window_data):
"""聚合窗口内的数据"""
if not window_data:
return {}
aggregated = {
'window_start': window_data[0]['timestamp'],
'window_end': window_data[-1]['timestamp'],
'sample_count': len(window_data),
'cpu_avg': sum(m['cpu_percent'] for m in window_data) / len(window_data),
'cpu_max': max(m['cpu_percent'] for m in window_data),
'memory_avg': sum(m['memory_used'] for m in window_data) / len(window_data),
'disk_io_avg': sum(m['disk_io'] for m in window_data) / len(window_data),
'network_rx_total': sum(m['network_rx'] for m in window_data),
'network_tx_total': sum(m['network_tx'] for m in window_data),
'connections_avg': sum(m['active_connections'] for m in window_data) / len(window_data)
}
# 检测异常(简单的阈值检测)
aggregated['anomalies'] = self._detect_anomalies(aggregated)
return aggregated
def _detect_anomalies(self, aggregated):
"""检测指标异常"""
anomalies = []
if aggregated['cpu_avg'] > 80:
anomalies.append('high_cpu')
if aggregated['cpu_max'] > 95:
anomalies.append('cpu_spike')
if aggregated['memory_avg'] > 7000:
anomalies.append('high_memory')
if aggregated['connections_avg'] > 8000:
anomalies.append('high_connections')
return anomalies
def multi_level_aggregation(self, raw_metrics_stream):
"""多级聚合:原始数据 -> 1秒窗口 -> 1分钟窗口 -> 5分钟窗口"""
# 第一级:1秒窗口聚合
one_sec_aggregated = self.sliding_window_aggregator(
raw_metrics_stream, window_seconds=1
)
# 第二级:1分钟窗口聚合(基于1秒聚合结果)
one_min_aggregated = self.sliding_window_aggregator(
one_sec_aggregated, window_seconds=60
)
# 第三级:5分钟窗口聚合(基于1分钟聚合结果)
five_min_aggregated = self.sliding_window_aggregator(
one_min_aggregated, window_seconds=300
)
return {
'raw': raw_metrics_stream,
'1s': one_sec_aggregated,
'1m': one_min_aggregated,
'5m': five_min_aggregated
}
# 使用示例
def monitor_system():
aggregator = MetricsAggregator()
# 生成模拟监控数据流
raw_metrics = aggregator.metrics_generator(interval=0.1)
# 获取多级聚合数据流
aggregation_streams = aggregator.multi_level_aggregation(raw_metrics)
# 处理不同粒度的数据
import itertools
for i, (one_sec, one_min, five_min) in enumerate(zip(
aggregation_streams['1s'],
aggregation_streams['1m'],
aggregation_streams['5m']
)):
print(f"\n--- Sample {i} ---")
print(f"1s聚合: CPU={one_sec['cpu_avg']:.1f}%")
print(f"1m聚合: CPU={one_min['cpu_avg']:.1f}%, 异常={one_min['anomalies']}")
print(f"5m聚合: CPU={five_min['cpu_avg']:.1f}%")
if i >= 10: # 只显示前10个样本
break
# monitor_system()分布式协调
import threading
import queue
import time
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
from typing import List, Dict, Any, Generator
class DistributedTaskCollector:
def __init__(self, worker_nodes: List[str], max_workers=10):
self.worker_nodes = worker_nodes
self.task_queue = queue.Queue()
self.result_queue = queue.Queue()
self.max_workers = max_workers
def submit_tasks(self, tasks: List[Dict]):
"""提交任务到队列"""
for task in tasks:
self.task_queue.put(task)
# 添加结束标记
for _ in range(len(self.worker_nodes)):
self.task_queue.put(None)
def worker(self, node_id: str) -> Generator[Dict, None, None]:
"""工作节点模拟,返回结果生成器"""
while True:
try:
task = self.task_queue.get(timeout=1)
if task is None:
break
# 模拟任务处理
result = self._process_task(task, node_id)
yield result
except queue.Empty:
continue
def _process_task(self, task: Dict, node_id: str) -> Dict:
"""模拟任务处理"""
# 模拟处理时间
processing_time = random.uniform(0.1, 2.0)
time.sleep(processing_time)
# 模拟任务结果
return {
'task_id': task['id'],
'node_id': node_id,
'result': f"Processed {task['data']}",
'processing_time': processing_time,
'success': random.random() > 0.1, # 90%成功率
'timestamp': datetime.now()
}
def result_collector(self) -> Generator[Dict, None, None]:
"""收集所有工作节点的结果"""
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=self.max_workers) as executor:
# 启动所有工作节点
future_to_node = {
executor.submit(self._run_worker, node): node
for node in self.worker_nodes
}
# 收集结果
completed = 0
while completed < len(self.worker_nodes):
for future in future_to_node:
if future.done():
try:
# 获取工作节点的所有结果
for result in future.result():
yield result
except Exception as e:
yield {
'error': str(e),
'node_id': future_to_node[future],
'timestamp': datetime.now()
}
completed += 1
break
time.sleep(0.1)
def _run_worker(self, node_id: str) -> List[Dict]:
"""运行工作节点并收集其所有结果"""
return list(self.worker(node_id))
def real_time_aggregator(self, result_stream, window_size=100):
"""实时聚合任务执行结果"""
results_window = deque(maxlen=window_size)
stats = {
'total_processed': 0,
'success_count': 0,
'failure_count': 0,
'total_processing_time': 0.0,
'node_stats': defaultdict(lambda: {'processed': 0, 'success': 0})
}
for result in result_stream:
if 'error' in result:
stats['failure_count'] += 1
continue
results_window.append(result)
stats['total_processed'] += 1
if result['success']:
stats['success_count'] += 1
else:
stats['failure_count'] += 1
stats['total_processing_time'] += result['processing_time']
# 更新节点统计
node_id = result['node_id']
stats['node_stats'][node_id]['processed'] += 1
if result['success']:
stats['node_stats'][node_id]['success'] += 1
# 定期输出统计信息
if stats['total_processed'] % 10 == 0:
yield self._compute_real_time_stats(stats, list(results_window))
# 最终统计
yield self._compute_real_time_stats(stats, list(results_window))
def _compute_real_time_stats(self, stats, recent_results):
"""计算实时统计信息"""
if stats['total_processed'] == 0:
return {}
avg_processing_time = (
stats['total_processing_time'] / stats['total_processed']
)
success_rate = (
stats['success_count'] / stats['total_processed'] * 100
)
# 计算最近结果的趋势
recent_success_rate = 0
if recent_results:
recent_success = sum(1 for r in recent_results if r.get('success'))
recent_success_rate = recent_success / len(recent_results) * 100
return {
'timestamp': datetime.now(),
'total_processed': stats['total_processed'],
'success_rate': success_rate,
'recent_success_rate': recent_success_rate,
'avg_processing_time': avg_processing_time,
'node_performance': {
node: {
'processed': data['processed'],
'success_rate': (
data['success'] / data['processed'] * 100
if data['processed'] > 0 else 0
)
}
for node, data in stats['node_stats'].items()
}
}
# 使用示例
def run_distributed_workload():
# 创建任务收集器
worker_nodes = [f'worker-{i}' for i in range(5)]
collector = DistributedTaskCollector(worker_nodes)
# 创建测试任务
tasks = [{'id': i, 'data': f'task_data_{i}'} for i in range(50)]
collector.submit_tasks(tasks)
# 收集并实时分析结果
result_stream = collector.result_collector()
stats_stream = collector.real_time_aggregator(result_stream)
print("开始处理分布式任务...")
for stats in stats_stream:
print(f"\n实时统计:")
print(f" 总处理数: {stats['total_processed']}")
print(f" 成功率: {stats['success_rate']:.1f}%")
print(f" 最近成功率: {stats['recent_success_rate']:.1f}%")
print(f" 平均处理时间: {stats['avg_processing_time']:.3f}s")
print(" 节点性能:")
for node, perf in stats['node_performance'].items():
print(f" {node}: {perf['processed']} tasks, "
f"{perf['success_rate']:.1f}% success")
# run_distributed_workload()Python with 语句
基本概念是
with 语句进行的是包装一个代码块的执行,允许定义初始化和清理操作吧,通常用于资源管理
上下文协议
__enter__(self)进入 with 语句的时候实现调用的语句吧,返回的是一个对象讷,该对象一般为了方便操作 as 赋值给对应的变量__exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, tracebakc)离开的时候实现的对应的执行函数吧,异常类型或者说异常值的跟踪吧
工作原理
调用上下文管理器
__enter__如果指定了 as 子句,直接进行返回值赋值的变量吧
执行 with 语句代码块
无论是否发生异常都会执行
__exit__,返回 True 就不会进行传播异常吧,否则就是有异常讷
from contextlib import contextmanager
import time
import psutil
import threading
@contextmanager
def resource_monitor(description="操作"):
"""资源监控上下文管理器"""
process = psutil.Process()
# 初始资源使用
start_memory = process.memory_info().rss / 1024 / 1024 # MB
start_cpu = process.cpu_percent()
start_time = time.time()
# 监控线程
stop_monitoring = threading.Event()
peak_memory = start_memory
def monitor_resources():
nonlocal peak_memory
while not stop_monitoring.is_set():
current_memory = process.memory_info().rss / 1024 / 1024
peak_memory = max(peak_memory, current_memory)
time.sleep(0.1)
monitor_thread = threading.Thread(target=monitor_resources)
monitor_thread.start()
try:
yield
finally:
stop_monitoring.set()
monitor_thread.join()
# 计算最终资源使用
end_time = time.time()
end_memory = process.memory_info().rss / 1024 / 1024
end_cpu = process.cpu_percent()
print(f"\n=== {description} 资源报告 ===")
print(f"执行时间: {end_time - start_time:.3f}秒")
print(f"内存使用: {start_memory:.1f}MB -> {end_memory:.1f}MB")
print(f"内存峰值: {peak_memory:.1f}MB")
print(f"CPU使用: {end_cpu:.1f}%")
@contextmanager
def query_logger(slow_query_threshold=1.0):
"""数据库查询日志上下文管理器"""
queries = []
start_time = time.time()
def log_query(query, params=None, duration=0):
queries.append({
'query': query,
'params': params,
'duration': duration,
'slow': duration > slow_query_threshold
})
try:
yield log_query
finally:
end_time = time.time()
total_time = end_time - start_time
print(f"\n=== 查询执行报告 ===")
print(f"总查询数: {len(queries)}")
print(f"总执行时间: {total_time:.3f}秒")
print(f"慢查询数: {sum(1 for q in queries if q['slow'])}")
for i, query in enumerate(queries, 1):
status = "🚨 慢查询" if query['slow'] else "✅ 正常"
print(f"{i}. [{status}] {query['duration']:.3f}s - {query['query']}")
# 使用示例
def process_large_dataset():
with resource_monitor("大数据处理"):
data = []
for i in range(100000):
data.append({"id": i, "value": i ** 2})
# 模拟耗时操作
time.sleep(2)
result = [item for item in data if item["id"] % 2 == 0]
return result
def mock_database_operations():
with query_logger(slow_query_threshold=0.5) as log_query:
# 模拟查询
queries = [
("SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = %s", (1,), 0.1),
("SELECT * FROM orders WHERE user_id = %s", (1,), 0.3),
("SELECT COUNT(*) FROM large_table", None, 1.2), # 慢查询
("UPDATE products SET price = price * 1.1", None, 0.8),
]
for query, params, duration in queries:
time.sleep(duration) # 模拟查询时间
log_query(query, params, duration)
# process_large_dataset()
# mock_database_operations()import tempfile
import shutil
from contextlib import contextmanager
import os
@contextmanager
def temporary_directory(prefix="tmp_"):
"""临时目录上下文管理器"""
temp_dir = tempfile.mkdtemp(prefix=prefix)
try:
print(f"创建临时目录: {temp_dir}")
yield temp_dir
finally:
print(f"清理临时目录: {temp_dir}")
shutil.rmtree(temp_dir)
@contextmanager
def change_directory(path):
"""临时切换工作目录"""
original_cwd = os.getcwd()
try:
os.chdir(path)
print(f"切换到目录: {path}")
yield
finally:
os.chdir(original_cwd)
print(f"切回目录: {original_cwd}")
@contextmanager
def environment_variables(**kwargs):
"""临时设置环境变量"""
original_env = {}
try:
# 保存原始值并设置新值
for key, value in kwargs.items():
original_env[key] = os.environ.get(key)
os.environ[key] = str(value)
print(f"设置环境变量: {key}={value}")
yield
finally:
# 恢复原始值
for key, original_value in original_env.items():
if original_value is None:
os.environ.pop(key, None)
print(f"删除环境变量: {key}")
else:
os.environ[key] = original_value
print(f"恢复环境变量: {key}={original_value}")
# 使用示例:复杂的构建流程
def build_project():
with temporary_directory(prefix="build_") as temp_dir:
with change_directory(temp_dir):
with environment_variables(
BUILD_MODE="production",
NODE_ENV="production",
DEBUG="false"
):
# 执行构建命令
print("开始构建项目...")
# os.system("npm run build")
# os.system("python setup.py build")
print("构建完成")
# 这里临时目录会自动清理
print("所有资源已清理")
# build_project()from contextlib import contextmanager
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
class DatabaseManager:
def __init__(self, connection_string):
self.engine = create_engine(connection_string)
self.Session = sessionmaker(bind=self.engine)
@contextmanager
def transaction(self, auto_commit=True):
"""数据库事务上下文管理器"""
session = self.Session()
try:
yield session
if auto_commit:
session.commit()
print("事务提交成功")
except Exception as e:
session.rollback()
print(f"事务回滚: {e}")
raise
finally:
session.close()
@contextmanager
def nested_transaction(self):
"""嵌套事务支持"""
session = self.Session()
try:
# 开始嵌套事务
session.begin_nested()
yield session
session.commit()
print("嵌套事务提交")
except Exception as e:
session.rollback()
print(f"嵌套事务回滚: {e}")
raise
finally:
session.close()
# 使用示例
db = DatabaseManager("sqlite:///example.db")
# 基本事务
with db.transaction() as session:
user = User(name="张三", email="zhangsan@example.com")
session.add(user)
# 如果这里发生异常,事务会自动回滚
# 复杂业务逻辑
with db.transaction() as session:
# 创建用户
user = User(name="李四", email="lisi@example.com")
session.add(user)
session.flush() # 获取用户ID
# 创建用户配置
profile = UserProfile(user_id=user.id, settings={"theme": "dark"})
session.add(profile)
# 记录创建日志
log = AuditLog(action="user_created", user_id=user.id)
session.add(log)
# 所有操作要么全部成功,要么全部回滚class DatabaseConnection:
def __init__(self, db_url):
self.db_url = db_url
self.connection = None
self.transaction_count = 0
def __enter__(self):
print(f"连接到数据库: {self.db_url}")
self.connection = self._create_connection()
self.transaction_count = 0
return self
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):
if exc_type is not None:
print(f"发生异常: {exc_type.__name__}: {exc_val}")
self.connection.rollback()
else:
self.connection.commit()
print("关闭数据库连接")
self.connection.close()
# 返回 True 表示异常已被处理,不再向上传播
return False # 让异常正常传播
def _create_connection(self):
# 模拟创建数据库连接
class MockConnection:
def commit(self): print("提交事务")
def rollback(self): print("回滚事务")
def close(self): print("关闭连接")
def execute(self, query):
print(f"执行: {query}")
return f"结果: {query}"
return MockConnection()
def execute_query(self, query):
self.transaction_count += 1
return self.connection.execute(query)
# 使用示例
with DatabaseConnection("postgresql://localhost/mydb") as db:
result1 = db.execute_query("SELECT * FROM users")
result2 = db.execute_query("UPDATE products SET price = 100")
print(f"执行了 {db.transaction_count} 个事务")Python 装饰器
日志记录: 装饰器可用于记录函数的调用信息、参数和返回值。
性能分析: 可以使用装饰器来测量函数的执行时间。
权限控制: 装饰器可用于限制对某些函数的访问权限。
缓存: 装饰器可用于实现函数结果的缓存,以提高性能。
类装饰器基于我们的
__call__实现的吧
内置装饰器
@staticmethod: 将方法定义为静态方法,不需要实例化类即可调用。@classmethod: 将方法定义为类方法,第一个参数是类本身(通常命名为cls)。@property: 将方法转换为属性,使其可以像属性一样访问。
def logger_decorator(func):
"""记录函数参数和返回值的装饰器"""
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
print(f"调用函数: {func.__name__}")
print(f"参数: args={args}, kwargs={kwargs}")
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
print(f"返回值: {result}")
return result
return wrapper
@logger_decorator
def add(a, b):
return a + b
@logger_decorator
def greet(name, greeting="Hello"):
return f"{greeting}, {name}!"
# 使用
add(3, 5)
greet("Alice", greeting="Hi")
from functools import wraps
def preserve_metadata_decorator(func):
"""使用wraps保留原函数元信息"""
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
print(f"执行 {func.__name__}")
return func(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapper
@preserve_metadata_decorator
def example_function():
"""这是一个示例函数"""
pass
print(example_function.__name__) # example_function
print(example_function.__doc__) # 这是一个示例函数
class TimerDecorator:
"""计时器类装饰器"""
def __init__(self, func):
self.func = func
wraps(func)(self)
def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
import time
start_time = time.time()
result = self.func(*args, **kwargs)
end_time = time.time()
print(f"函数 {self.func.__name__} 执行时间: {end_time - start_time:.4f}秒")
return result
class RetryDecorator:
"""重试机制类装饰器"""
def __init__(self, max_retries=3, delay=1):
self.max_retries = max_retries
self.delay = delay
def __call__(self, func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
import time
last_exception = None
for attempt in range(self.max_retries):
try:
return func(*args, **kwargs)
except Exception as e:
last_exception = e
print(f"尝试 {attempt + 1} 失败: {e}")
if attempt < self.max_retries - 1:
print(f"等待 {self.delay} 秒后重试...")
time.sleep(self.delay)
print(f"所有 {self.max_retries} 次尝试均失败")
raise last_exception
return wrapper
# 使用类装饰器
@TimerDecorator
def slow_function():
import time
time.sleep(1)
return "完成"
@RetryDecorator(max_retries=3, delay=2)
def unreliable_network_call():
import random
if random.random() < 0.7: # 70% 失败率
raise ConnectionError("网络连接失败")
return "成功"
# 使用
slow_function()
try:
unreliable_network_call()
except Exception as e:
print(f"最终失败: {e}")
from functools import wraps
from flask import request, jsonify, g
import jwt
def login_required(f):
"""登录验证装饰器"""
@wraps(f)
def decorated_function(*args, **kwargs):
token = request.headers.get('Authorization')
if not token:
return jsonify({'error': '缺少认证令牌'}), 401
try:
# 验证JWT令牌
payload = jwt.decode(token, 'secret-key', algorithms=['HS256'])
g.user_id = payload['user_id']
g.user_role = payload.get('role', 'user')
except jwt.ExpiredSignatureError:
return jsonify({'error': '令牌已过期'}), 401
except jwt.InvalidTokenError:
return jsonify({'error': '无效令牌'}), 401
return f(*args, **kwargs)
return decorated_function
def role_required(required_role):
"""角色权限装饰器"""
def decorator(f):
@wraps(f)
def decorated_function(*args, **kwargs):
# 假设用户信息已经通过 login_required 设置到 g 对象中
if not hasattr(g, 'user_role') or g.user_role != required_role:
return jsonify({'error': '权限不足'}), 403
return f(*args, **kwargs)
return decorated_function
return decorator
def rate_limit(requests_per_minute=60):
"""API限流装饰器"""
import time
from collections import defaultdict
request_timestamps = defaultdict(list)
def decorator(f):
@wraps(f)
def decorated_function(*args, **kwargs):
# 获取客户端标识(这里简单使用IP)
client_ip = request.remote_addr
current_time = time.time()
# 清理1分钟前的记录
request_timestamps[client_ip] = [
ts for ts in request_timestamps[client_ip]
if current_time - ts < 60
]
# 检查是否超过限制
if len(request_timestamps[client_ip]) >= requests_per_minute:
return jsonify({
'error': '请求过于频繁',
'retry_after': 60
}), 429
# 记录本次请求
request_timestamps[client_ip].append(current_time)
return f(*args, **kwargs)
return decorated_function
return decorator
# 在Flask路由中使用
@app.route('/api/admin/users')
@login_required
@role_required('admin')
@rate_limit(requests_per_minute=30)
def get_all_users():
# 只有管理员才能访问,且受到限流保护
users = User.query.all()
return jsonify([user.to_dict() for user in users])
@app.route('/api/profile')
@login_required
@rate_limit(requests_per_minute=60)
def get_user_profile():
# 普通用户访问自己的资料,基础限流
user = User.query.get(g.user_id)
return jsonify(user.to_dict())
import time
from functools import wraps
import pickle
import hashlib
def cache(ttl=300, maxsize=1000):
"""缓存装饰器,支持TTL和最大缓存大小"""
cache_store = {}
cache_keys = [] # 用于LRU淘汰
def decorator(func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# 生成缓存键
key_data = pickle.dumps((args, sorted(kwargs.items())))
cache_key = hashlib.md5(key_data).hexdigest()
# 检查缓存
if cache_key in cache_store:
cached_data, timestamp = cache_store[cache_key]
if time.time() - timestamp < ttl:
print(f"缓存命中: {func.__name__}")
return cached_data
else:
# 缓存过期
del cache_store[cache_key]
cache_keys.remove(cache_key)
# 执行函数
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
# 更新缓存
if len(cache_store) >= maxsize:
# LRU淘汰
oldest_key = cache_keys.pop(0)
del cache_store[oldest_key]
cache_store[cache_key] = (result, time.time())
cache_keys.append(cache_key)
return result
return wrapper
return decorator
def async_timer(func):
"""异步函数计时装饰器"""
@wraps(func)
async def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start_time = time.time()
try:
result = await func(*args, **kwargs)
return result
finally:
end_time = time.time()
print(f"异步函数 {func.__name__} 执行时间: {end_time - start_time:.4f}秒")
return wrapper
def database_query_logger(func):
"""数据库查询日志装饰器"""
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start_time = time.time()
try:
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
execution_time = time.time() - start_time
# 记录慢查询
if execution_time > 1.0: # 1秒以上认为是慢查询
print(f"🚨 慢查询警告: {func.__name__} 耗时 {execution_time:.3f}秒")
return result
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 查询错误: {func.__name__} - {e}")
raise
return wrapper
# 使用示例
@cache(ttl=600) # 缓存10分钟
@database_query_logger
def get_user_by_id(user_id):
# 模拟数据库查询
time.sleep(0.5)
return {"id": user_id, "name": f"User {user_id}"}
@async_timer
async def fetch_user_data_async(user_id):
import asyncio
await asyncio.sleep(0.3)
return {"id": user_id, "data": "some_data"}
from functools import wraps
import jsonschema
from marshmallow import Schema, fields, ValidationError
def validate_json_schema(schema):
"""JSON Schema验证装饰器"""
def decorator(func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# 假设第一个参数是请求数据
if args and isinstance(args[0], dict):
data = args[0]
try:
jsonschema.validate(instance=data, schema=schema)
except jsonschema.ValidationError as e:
raise ValueError(f"数据验证失败: {e.message}")
return func(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapper
return decorator
def validate_with_marshmallow(schema_class):
"""使用Marshmallow进行数据验证"""
def decorator(func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
if args and isinstance(args[0], dict):
data = args[0]
schema = schema_class()
try:
validated_data = schema.load(data)
# 用验证后的数据替换原始数据
new_args = (validated_data,) + args[1:]
return func(*new_args, **kwargs)
except ValidationError as e:
raise ValueError(f"数据验证失败: {e.messages}")
return func(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapper
return decorator
def transform_response(serializer_class):
"""响应数据序列化装饰器"""
def decorator(func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
# 序列化结果
if result is not None:
serializer = serializer_class()
if isinstance(result, list):
return [serializer.dump(item) for item in result]
else:
return serializer.dump(result)
return result
return wrapper
return decorator
# 定义数据模式
class UserSchema(Schema):
id = fields.Int(required=True)
name = fields.Str(required=True)
email = fields.Email(required=True)
class UserCreateSchema(Schema):
name = fields.Str(required=True, validate=lambda x: len(x) >= 2)
email = fields.Email(required=True)
password = fields.Str(required=True, validate=lambda x: len(x) >= 6)
# 使用示例
user_create_schema = {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {"type": "string", "minLength": 2},
"email": {"type": "string", "format": "email"},
"password": {"type": "string", "minLength": 6}
},
"required": ["name", "email", "password"]
}
@validate_json_schema(user_create_schema)
# 或者使用 @validate_with_marshmallow(UserCreateSchema)
def create_user(user_data):
# 这里user_data已经通过验证
user = User(**user_data)
user.save()
return user
@transform_response(UserSchema)
def get_user(user_id):
user = User.query.get(user_id)
return user
import psutil
import threading
from functools import wraps
from contextlib import contextmanager
def circuit_breaker(failure_threshold=5, recovery_timeout=60):
"""断路器装饰器,防止级联故障"""
state = {
'failures': 0,
'last_failure_time': None,
'state': 'CLOSED' # CLOSED, OPEN, HALF_OPEN
}
lock = threading.Lock()
def decorator(func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
with lock:
current_time = time.time()
# 检查断路器状态
if state['state'] == 'OPEN':
if (current_time - state['last_failure_time']) > recovery_timeout:
state['state'] = 'HALF_OPEN'
else:
raise CircuitBreakerError("断路器打开,服务暂时不可用")
try:
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
# 成功调用,重置断路器
with lock:
if state['state'] == 'HALF_OPEN':
state['state'] = 'CLOSED'
state['failures'] = 0
return result
except Exception as e:
with lock:
state['failures'] += 1
state['last_failure_time'] = current_time
if state['failures'] >= failure_threshold:
state['state'] = 'OPEN'
raise CircuitBreakerError(f"调用失败,断路器状态: {state['state']}") from e
return wrapper
return decorator
def resource_monitor(cpu_threshold=80, memory_threshold=80):
"""资源监控装饰器,在资源紧张时降级"""
def decorator(func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# 检查系统资源
cpu_percent = psutil.cpu_percent(interval=1)
memory_percent = psutil.virtual_memory().percent
if cpu_percent > cpu_threshold or memory_percent > memory_threshold:
print(f"⚠️ 资源紧张: CPU {cpu_percent}%, 内存 {memory_percent}%")
# 可以在这里实现降级逻辑
if hasattr(func, 'fallback'):
return func.fallback(*args, **kwargs)
else:
raise ResourceWarning("系统资源紧张,服务降级")
return func(*args, **kwargs)
# 添加降级方法
def fallback(*args, **kwargs):
return {"status": "degraded", "message": "服务降级中"}
wrapper.fallback = fallback
return wrapper
return decorator
def distributed_lock(lock_key_func, timeout=30):
"""分布式锁装饰器"""
def decorator(func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
lock_key = lock_key_func(*args, **kwargs)
# 这里使用Redis作为分布式锁(需要redis-py)
import redis
redis_client = redis.Redis()
lock_acquired = False
try:
# 尝试获取锁
lock_acquired = redis_client.set(
lock_key, 'locked', nx=True, ex=timeout
)
if not lock_acquired:
raise DistributedLockError(f"无法获取锁: {lock_key}")
return func(*args, **kwargs)
finally:
if lock_acquired:
redis_client.delete(lock_key)
return wrapper
return decorator
# 自定义异常
class CircuitBreakerError(Exception):
pass
class DistributedLockError(Exception):
pass
# 使用示例
@circuit_breaker(failure_threshold=3, recovery_timeout=30)
@resource_monitor(cpu_threshold=85, memory_threshold=90)
def process_payment(user_id, amount):
# 模拟支付处理
if amount > 1000:
raise ValueError("金额过大")
return {"status": "success", "transaction_id": "12345"}
# 为支付处理添加降级方法
def payment_fallback(user_id, amount):
return {"status": "pending", "message": "支付处理延迟"}
process_payment.fallback = payment_fallback
# 分布式锁使用
def order_lock_key(user_id, *args, **kwargs):
return f"lock:order:{user_id}"
@distributed_lock(lock_key_func=order_lock_key, timeout=60)
def create_order(user_id, items):
# 创建订单,确保同一用户不会并发创建多个订单
return {"order_id": "ORDER123", "status": "created"}python 标准库总结
os 模块:os 模块提供了许多与操作系统交互的函数,例如创建、移动和删除文件和目录,以及访问环境变量等。
sys 模块:sys 模块提供了与 Python 解释器和系统相关的功能,例如解释器的版本和路径,以及与 stdin、stdout 和 stderr 相关的信息。
time 模块:time 模块提供了处理时间的函数,例如获取当前时间、格式化日期和时间、计时等。
datetime 模块:datetime 模块提供了更高级的日期和时间处理函数,例如处理时区、计算时间差、计算日期差等。
random 模块:random 模块提供了生成随机数的函数,例如生成随机整数、浮点数、序列等。
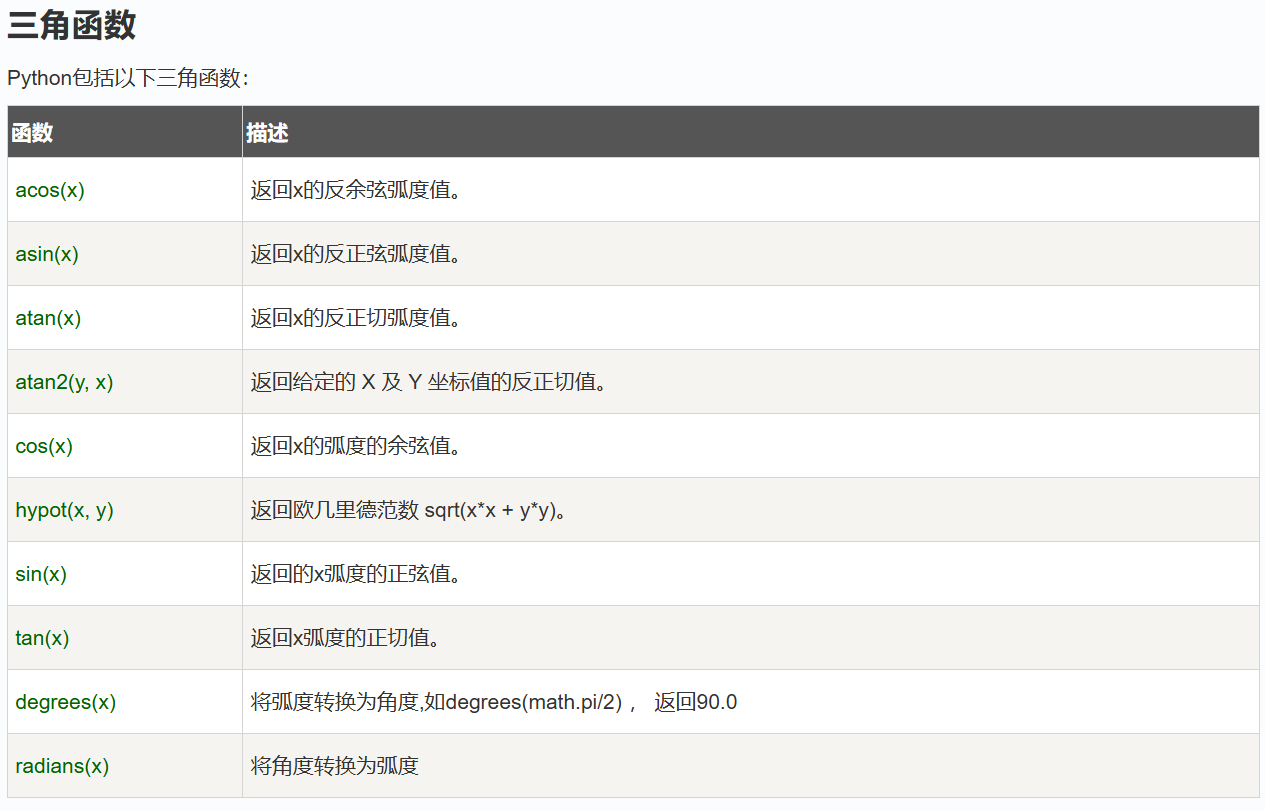
math 模块:math 模块提供了数学函数,例如三角函数、对数函数、指数函数、常数等。
re 模块:re 模块提供了正则表达式处理函数,可以用于文本搜索、替换、分割等。
json 模块:json 模块提供了 JSON 编码和解码函数,可以将 Python 对象转换为 JSON 格式,并从 JSON 格式中解析出 Python 对象。
urllib 模块:urllib 模块提供了访问网页和处理 URL 的功能,包括下载文件、发送 POST 请求、处理 cookies 等
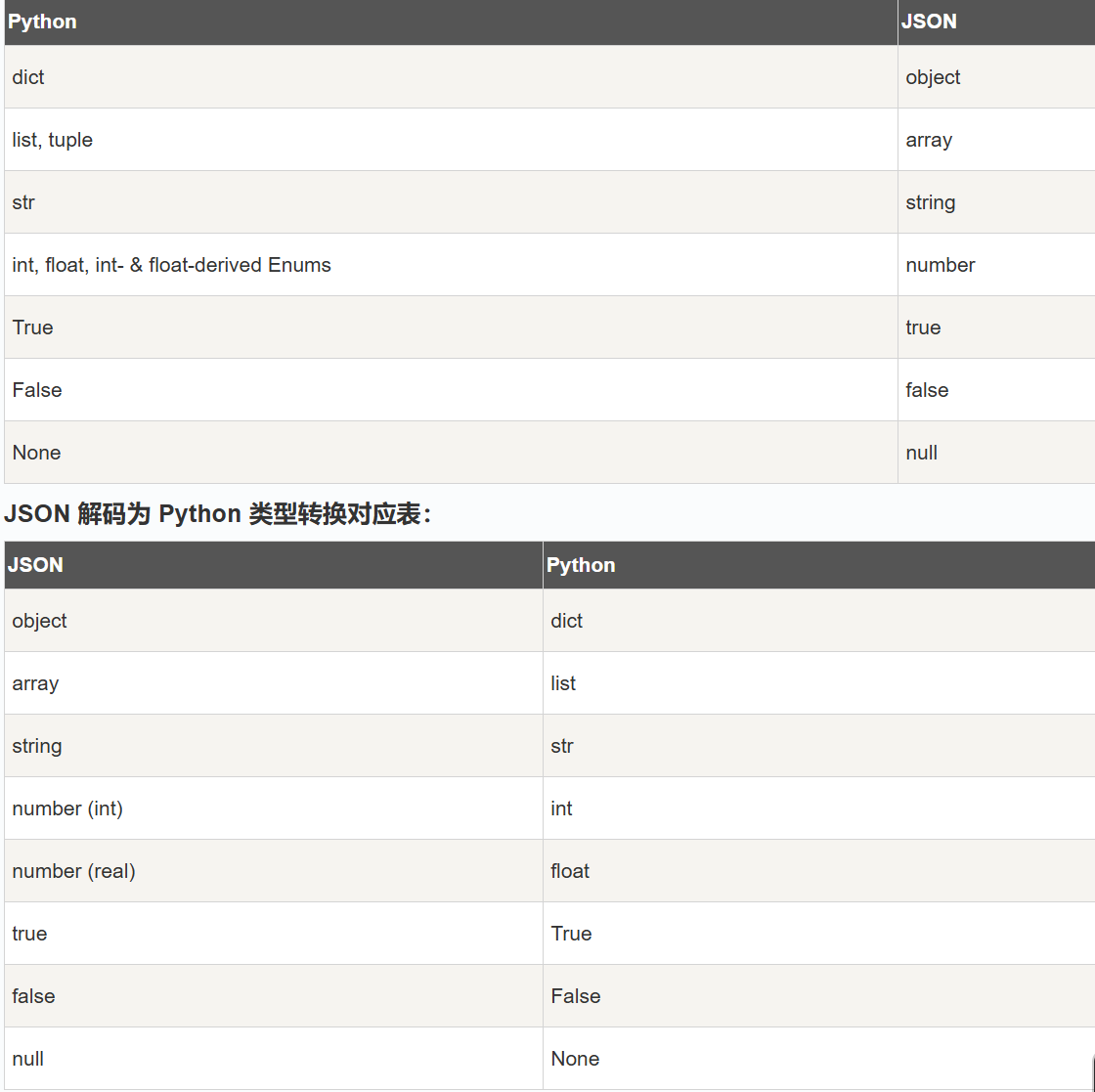
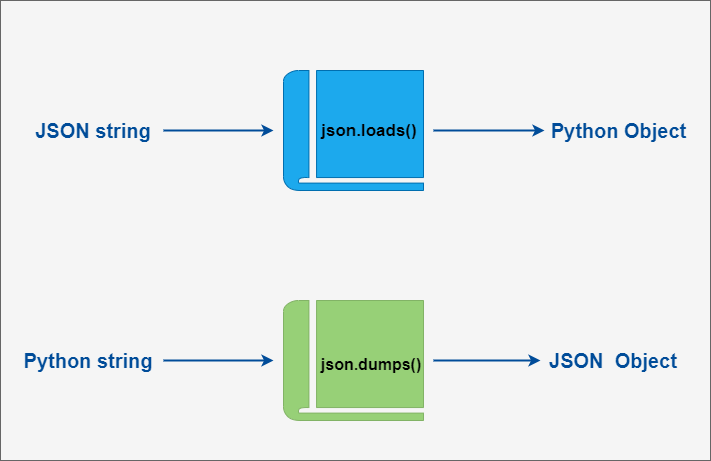
Python json 模块